SAMA7G5-EK Board
SoC Features
The SAMA7G54 is a high-performance, ultra-low power Arm Cortex-A7 CPU-based embedded microprocessor (MPU) running up to 1 GHz. It supports multiple memories such as 16-bit DDR2, DDR3, DDR3L, LPDDR2, LPDDR3 with flexible boot options from octal/quad SPI, SD/eMMC as well as 8-bit SLC/MLC NAND Flash.
The SAMA7G54 integrates complete imaging and audio subsystems with 12-bit parallel and/or MIPI-CSI2 camera interfaces supporting up to 8 Mpixels and 720p @ 30 fps, up to four I2S, one SPDIF transmitter and receiver and a 4-stereo channel audio sample rate converter.
The device also features a large number of connectivity options including Dual Ethernet (one Gigabit Ethernet and one 10/100 Ethernet), six CAN-FD and three high-speed USB. Advanced security functions like secure boot, secure key storage, high-performance crypto accelerators for AES, SHA, RSA and ECC are also supported.
Microchip provides an optimized power management solution for the SAMA7G54. The MCP16502 has been fully tested and optimized to provide the best power vs. performance for the SAMA7G54.
Kit Information
Kit Overview
The SAMA7G5 Evaluation Kit (SAMA7G5-EK) provides a versatile Total System Solution platform that highlights Microchip MPU and connectivity ICs.
The board features on-board memories, two Ethernet interfaces, three USB ports, two CAN interfaces, one SD card connector, two mikroBUS™ click interface headers to support over 450 MikroElektronika Click boards™, an RPi CSIcamera to support a camera module, an RPi extension connector to support several extension boards, and provision to solder a Microchip ATWILC3000-MR110xA Wi-Fi/Bluetooth module.
Note: RPi stands for “Raspberry Pi”. Raspberry Pi is a trademark of Raspberry Pi Trading.
The Kit is supported by mainline Linux distribution as well as bare metal software frameworks allowing you to easily get started with your development.
|
|
Access the console
The usual serial communication parameters are 115200 8-N-1 :
|
|||||||||||
Access the console on DEBUG serial port
The serial console can be accessed from the DEBUG port with the help of a TTL-to-USB serial cable (marked as DEBUG J20).
Using DEBUG on TTL-to-USB connector (DEBUG J20)
- For Microsoft Windows users: Install the driver of your USB TTL serial cable. FTDI-based ones are the most popular, have a look to this page to get the driver: http://www.ftdichip.com/Drivers/VCP.htm
 * Be sure to connect a 3.3V compatible cable and identify its GND pin. Place it properly according to the silkscreen and connect the cable to the board (J20)
* Be sure to connect a 3.3V compatible cable and identify its GND pin. Place it properly according to the silkscreen and connect the cable to the board (J20) - For Microsoft Windows users: identify the USB connection that is established
JLINK CDC UART Portshould appear in Device Manager. TheCOMxxnumber will be used to configure the terminal emulator.
- For Linux users: Identify the serial USB connection by monitoring the last lines of
dmesgcommand. The/dev/ttyUSBxnumber will be used to configure the terminal emulator.[605576.562740] usb 1-1.1.2: new full-speed USB device number 17 using ehci-pci [605576.660920] usb 1-1.1.2: New USB device found, idVendor=0403, idProduct=6001 [605576.660933] usb 1-1.1.2: New USB device strings: Mfr=1, Product=2, SerialNumber=3 [605576.660939] usb 1-1.1.2: Product: TTL232R-3V3 [605576.660944] usb 1-1.1.2: Manufacturer: FTDI [605576.660958] usb 1-1.1.2: SerialNumber: FTGNVZ04 [605576.663092] ftdi_sio 1-1.1.2:1.0: FTDI USB Serial Device converter detected [605576.663120] usb 1-1.1.2: Detected FT232RL [605576.663122] usb 1-1.1.2: Number of endpoints 2 [605576.663124] usb 1-1.1.2: Endpoint 1 MaxPacketSize 64 [605576.663126] usb 1-1.1.2: Endpoint 2 MaxPacketSize 64 [605576.663128] usb 1-1.1.2: Setting MaxPacketSize 64 [605576.663483] usb 1-1.1.2: FTDI USB Serial Device converter now attached to ttyUSB0A /dev/ttyUSB0 node has been created.
- For Microsoft Windows users: identify the USB connection that is established
- Now open your favorite terminal emulator with appropriate settings
Demo
Demo archives
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Create a SD card with the demo
You need a 1 GB SD card (or more) and to download the image of the demo. The image is compressed to reduce the amount of data to download. This image contains:
- a FAT32 partition with the AT91Bootstrap, U-Boot and the Linux Kernel (zImage and dtb).
- an EXT4 partition for the rootfs.
Multi-platform procedure
To write the compressed image on the SD card, you will have to download and install balenaEtcher![]() . This tool, which is an Open Source software, is useful since it allows to get a compressed image as input. More information and extra help available on the balenaEtcher website
. This tool, which is an Open Source software, is useful since it allows to get a compressed image as input. More information and extra help available on the balenaEtcher website![]() .
.
- Insert your SD card and launch
Etcher:
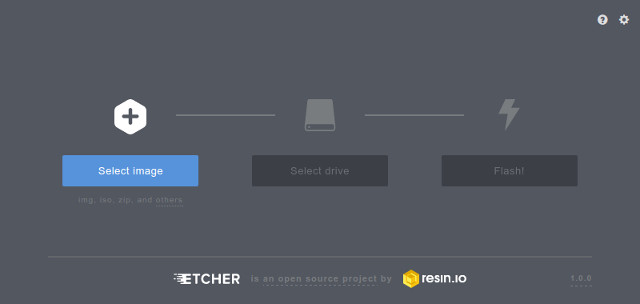
- Select the demo image. They are marked as "SD Card image" in the demo table above.
Note that you can select a compressed image (like the demos available here). The tool is able to decompress files on the fly - Select the device corresponding to your SD card (Etcher proposes you the devices that are removable to avoid erasing your system disk)
- Click on the
Flash!button - On Linux, Etcher finally asks you to enter your root password because it needs access to the hardware (your SD card reader or USB to SD card converter)
- then the flashing process begins followed by a verification phase (optional)
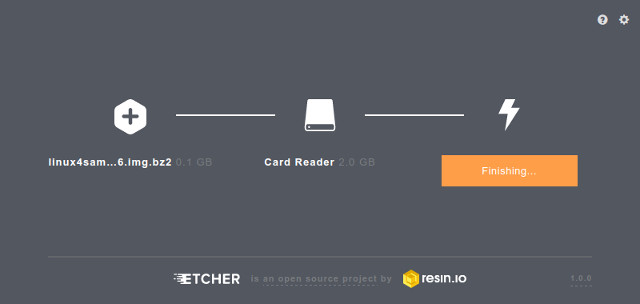
- Once writing done, Etcher asks you if you want to burn another demo image:

- Your SD card is ready!
Flash the demo
![]() If you need to store the root filesystem on a SD Card, use information contained in StroreRootFSonSD. This is useful for Linux4SAM demos older than 5.6.
If you need to store the root filesystem on a SD Card, use information contained in StroreRootFSonSD. This is useful for Linux4SAM demos older than 5.6.
![]() use SAM-BA 3.5.y onwards. You can download it here: SAM-BA 3.x release page
use SAM-BA 3.5.y onwards. You can download it here: SAM-BA 3.x release page![]() .
.
Run script to flash the demo
- download the demo package for the board. They are marked as "Media type: Boot on eMMC" in the table above
- extract the demo package
- run your usual terminal emulator and enter the demo directory
- make sure that the
sam-baapplication is in your Operating System path so that you can reach it from your demo package directory - for Microsoft Windows users: Launch the
demo_linux_emmcflash.batfile - for Linux users: Launch the
demo_linux_emmcflash.shfile - this script runs SAM-BA 3 and the associated
QMLsam-ba script (demo_linux_emmcflash_usb.qml) with proper parameters - when you reach the end of the flashing process (this will take a few minutes), the following line is written:
-I- === Done. ===
- connect a serial link on DBGU and open the terminal emulator program as explained just above
- power cycle the board
- WARNING: By default, the ROM code on the MPU does not boot from eMMC device (SDMMC0). Please refer to product datasheet on how to configure the ROM code boot configuration to enable booting from SDMMC0, either by writing the OTP (one-time programmable memory) with a boot package to boot from SDMMC0, or to enable emulation mode and in emulation mode to enable booting from SDMMC0. This configuration can be achieved using
sam-batool. - monitor the system while it's booting on the LCD screen or through the serial line
Build From source code
Setup ARM Cross Compiler
- First step is to dowload the ARM GNU Toolchain:
wget -c https://developer.arm.com/-/media/Files/downloads/gnu/13.2.rel1/binrel/arm-gnu-toolchain-13.2.rel1-x86_64-arm-none-linux-gnueabihf.tar.xz
- Next step is to add the ARM GNU Toolchain into your system:
tar -xf arm-gnu-toolchain-13.2.rel1-x86_64-arm-none-linux-gnueabihf.tar.xz export CROSS_COMPILE=`pwd`/arm-gnu-toolchain-13.2.rel1-x86_64-arm-none-linux-gnueabihf/bin/arm-none-linux-gnueabihf-ortar -xf arm-gnu-toolchain-13.2.rel1-x86_64-arm-none-linux-gnueabihf.tar.xz export CROSS_COMPILE=arm-none-linux-gnueabihf- export PATH=$PATH:/YOUR/PATH/TO/arm-gnu-toolchain-13.2.Rel1-x86_64-arm-none-linux-gnueabihf/bin/
- !Note: If you already have an old ARM GNU Toolchain need to clean up the PATH with:
export PATH=${PATH/':/YOUR/PATH/TO/arm-gnu-toolchain-VERSION-x86_64-arm-none-linux-gnueabihf/bin/'/}
Build AT91Bootstrap from sources
This section describes how to get source code from the git repository, how to configure with the default configuration, how to customize AT91Bootstrap based on the default configuration and finally to build AT91Bootstrap to produce the binary. take the default configuration to download U-Boot from NandFlash for example.
Get AT91Bootstrap Source Code
You can easily download AT91Bootstrap source code on the at91bootstrapTo get the source code, you should clone the repository by doing:
$ git clone https://github.com/linux4sam/at91bootstrap.git Cloning into 'at91bootstrap'... remote: Enumerating objects: 17621, done. remote: Counting objects: 100% (3324/3324), done. remote: Compressing objects: 100% (1029/1029), done. remote: Total 17621 (delta 2465), reused 3102 (delta 2285), pack-reused 14297 Receiving objects: 100% (17621/17621), 5.65 MiB | 4.65 MiB/s, done. Resolving deltas: 100% (13459/13459), done. $ cd at91bootstrap/
Configure AT91Bootstrap
Customize AT91Bootstrap
If the default configuration doesn't meet your need, after configuring with the default configuration, you can customize it by doing:$ make menuconfigNow, in the menuconfig dialog, you can easily add or remove some features to/from AT91Bootstrap as the same way as kernel configuration.
Move to
<Exit> with arrows and press this button hitting the Enter key to exit from this screen.
Build AT91Bootstrap
Then you can build the AT91Bootstrap binary by doing:$ make
If the building process is successful, the final .bin image is build/binaries/at91bootstrap.bin.
Build U-Boot from sources
Getting U-Boot sources
Dedicated page on U-Boot wiki: http://www.denx.de/wiki/U-Boot/SourceCode![]()
You can easily download U-Boot source code from Linux4Microchip GitHub U-Boot repository![]() :
:
- clone the Linux4microchip GitHub U-Boot repository
$ git clone https://github.com/linux4microchip/u-boot-mchp.git Cloning into 'u-boot-mchp'... remote: Enumerating objects: 951876, done. remote: Counting objects: 100% (17718/17718), done. remote: Compressing objects: 100% (5735/5735), done. remote: Total 951876 (delta 12391), reused 15314 (delta 11846), pack-reused 934158 Receiving objects: 100% (951876/951876), 164.77 MiB | 401.00 KiB/s, done. Resolving deltas: 100% (790362/790362), done. $ cd u-boot-mchp/
- The source code has been taken from the master branch which is pointing to the latest branch we use. If you want to use the other branch, you can list them and use one of them by doing:
$ git branch -r origin/HEAD -> origin/master origin/dev/tony/sama7g5ek_optee origin/master origin/sam9x60_curiosity_early origin/sam9x60_early origin/sam9x60_iar origin/sam9x7_early origin/sama5d27wlsom1ek_ear origin/sama7g5_early origin/u-boot-2012.10-at91 origin/u-boot-2013.07-at91 origin/u-boot-2014.07-at91 origin/u-boot-2015.01-at91 origin/u-boot-2016.01-at91 origin/u-boot-2016.03-at91 origin/u-boot-2017.03-at91 origin/u-boot-2018.07-at91 origin/u-boot-2019.04-at91 origin/u-boot-2020.01-at91 origin/u-boot-2021.04-at91 origin/u-boot-2022.01-at91 origin/u-boot-2023.07-mchp origin/u-boot-2024.07-mchp origin/uboot_5series_1.x $ git checkout origin/u-boot-2024.07-mchp -b u-boot-2024.07-mchp Branch 'u-boot-2024.07-mchp' set up to track remote branch 'u-boot-2024.07-mchp' from 'origin'. Switched to a new branch 'u-boot-2024.07-mchp'
Cross-compiling U-Boot
Before compiling the U-Boot, you need setup cross compile toolchain in the section.
![]() Latest versions of U-boot (2018.07 and newer) have a minimum requirement of 6.0 version of the GCC toolchain. We always recommend to use the latest versions.
Latest versions of U-boot (2018.07 and newer) have a minimum requirement of 6.0 version of the GCC toolchain. We always recommend to use the latest versions.
Once the AT91 U-Boot sources available, cross-compile U-Boot is made in two steps: configuration and compiling. Check the Configuration chapter![]() in U-Boot reference manual.
in U-Boot reference manual.
![]() Go to the
Go to the configs/ to find the exact target when invoking make.
The U-Boot environment variables can be stored in different media, above config files can specify where to store the U-Boot environment.
# To put environment variables in eMMC flash: sama7g5ek_mmc_defconfig # To put environment variables in SD/MMC card: sama7g5ek_mmc1_defconfig # To put environment variables in qspi flash: sama7g5ek_qspi0_defconfig
Here are the building steps for the SAMA7G5-EK board:
# You can change the config according to your needs. make sama7g5ek_mmc1_defconfig make
The result of these operations is a fresh U-Boot binary called u-boot.bin corresponding to the binary ELF file u-boot.
-
u-boot.binis the file you should store on the board -
u-bootis the ELF format binary file you may use to debug U-Boot through a JTag link for instance.
Build Kernel from sources
Required packages
You must install essential host packages on your build host. These requirements are listed in the Linux kernel documentation with the chapter Install build requirements
- build-essential
- flex
- bison
- git
- perl-base
- libssl-dev
- libncurses5-dev
- libncursesw5-dev
- ncurses-dev
Getting Kernel sources
To get the source code, you have to clone the repository:
$ git clone https://github.com/linux4microchip/linux.git Cloning into 'linux'... remote: Enumerating objects: 8587836, done. remote: Total 8587836 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 8587836 Receiving objects: 100% (8587836/8587836), 3.49 GiB | 13.44 MiB/s, done. Resolving deltas: 100% (7117887/7117887), done. Updating files: 100% (70687/70687), done. $ cd linux
The source code has been taken from the master branch which is pointing on the latest branch we use.
![]() Note that you can also add this Linux4SAM repository as a remote GIT repository
Note that you can also add this Linux4SAM repository as a remote GIT repository![]() to your usual Linux git tree. It will save you a lot of bandwidth and download time:
to your usual Linux git tree. It will save you a lot of bandwidth and download time:
$ git remote add linux4microchip https://github.com/linux4microchip/linux.git $ git remote update linux4microchip Fetching linux4microchip From https://github.com/linux4microchip/linux * [new branch] linux-6.1-mchp -> linux4microchip/linux-6.1-mchp * [new branch] linux-6.6-mchp -> linux4microchip/linux-6.6-mchp * [new branch] master -> linux4microchip/master
If you want to use another branch, you can list them and use one of them by doing this:
$ git branch -r linux4microchip/linux-5.10-mchp linux4microchip/linux-5.15-mchp linux4microchip/linux-5.15-mchp+fpga linux4microchip/linux-6.1-mchp linux4microchip/linux-6.1-mchp+fpga linux4microchip/linux-6.6-mchp linux4microchip/linux-6.6-mchp+fpga linux4microchip/master $ git checkout -b linux-6.6-mchp --track remotes/linux4microchip/linux-6.6-mchp Branch linux-6.6-mchp set up to track remote branch linux-6.6-mchp from linux4microchip. Switched to a new branch 'linux-6.6-mchp'
Setup ARM Cross Compiler
- First step is to dowload the ARM GNU Toolchain:
wget -c https://developer.arm.com/-/media/Files/downloads/gnu/13.2.rel1/binrel/arm-gnu-toolchain-13.2.rel1-x86_64-arm-none-linux-gnueabihf.tar.xz
- Next step is to add the ARM GNU Toolchain into your system:
tar -xf arm-gnu-toolchain-13.2.rel1-x86_64-arm-none-linux-gnueabihf.tar.xz export CROSS_COMPILE=`pwd`/arm-gnu-toolchain-13.2.rel1-x86_64-arm-none-linux-gnueabihf/bin/arm-none-linux-gnueabihf-ortar -xf arm-gnu-toolchain-13.2.rel1-x86_64-arm-none-linux-gnueabihf.tar.xz export CROSS_COMPILE=arm-none-linux-gnueabihf- export PATH=$PATH:/YOUR/PATH/TO/arm-gnu-toolchain-13.2.Rel1-x86_64-arm-none-linux-gnueabihf/bin/
- !Note: If you already have an old ARM GNU Toolchain need to clean up the PATH with:
export PATH=${PATH/':/YOUR/PATH/TO/arm-gnu-toolchain-VERSION-x86_64-arm-none-linux-gnueabihf/bin/'/}
Configure and Build the Linux kernel
Now you have to configure the Linux kernel according to your hardware. We have two default configuration at91 SoC inarch/arm/configs
arch/arm/configs/at91_dt_defconfig arch/arm/configs/sama5_defconfig arch/arm/configs/sama7_defconfig
-
at91_dt_defconfig: for SAM9 (ARM926) series chips -
sama5_defconfig: for SAMA5 series chips -
sama7_defconfig: for SAMA7 series chips
At this step, you can modify default configuration using the menuconfig
$ make ARCH=arm menuconfigNow, in the menuconfig dialog, you can easily add or remove some features. Once done, Move to
<Exit> with arrows and press this button hitting the Enter key to exit from this screen.
Build the Linux kernel image, before you build you need set up the cross compile toolchain, check this section.
$ make ARCH=arm [..] Kernel: arch/arm/boot/Image is ready Kernel: arch/arm/boot/zImage is ready
Now you have an usable compressed kernel image zImage.
If you need an uImage you can run this additional step:
make ARCH=arm uImage LOADADDR=0x20008000 [..] Kernel: arch/arm/boot/zImage is ready UIMAGE arch/arm/boot/uImage Image Name: Linux-6.6.23-linux4microchip-202 Created: Thu May 16 14:36:06 2024 Image Type: ARM Linux Kernel Image (uncompressed) Data Size: 5221704 Bytes = 5099.32 KiB = 4.98 MiB Load Address: 20008000 Entry Point: 20008000 Kernel: arch/arm/boot/uImage is ready
make ARCH=arm dtbs [..] DTC arch/arm/boot/dts/microchip/at91-sam9x60_curiosity.dtb DTC arch/arm/boot/dts/microchip/at91-sam9x60ek.dtb DTC arch/arm/boot/dts/microchip/at91-sam9x75_curiosity.dtb DTC arch/arm/boot/dts/microchip/at91-sam9x75eb.dtb DTC arch/arm/boot/dts/microchip/at91-sama5d27_som1_ek.dtb DTC arch/arm/boot/dts/microchip/at91-sama5d27_wlsom1_ek.dtb DTC arch/arm/boot/dts/microchip/at91-sama5d29_curiosity.dtb DTC arch/arm/boot/dts/microchip/at91-sama5d2_icp.dtb DTC arch/arm/boot/dts/microchip/at91-sama5d2_ptc_ek.dtb DTC arch/arm/boot/dts/microchip/at91-sama5d2_xplained.dtb DTC arch/arm/boot/dts/microchip/at91-sama7d65_curiosity.dtb DTC arch/arm/boot/dts/microchip/at91-sama7g5ek.dtb [..]
If the building process is successful, the final images can be found under arch/arm/boot/ directory.
Build Yocto/Poky rootfs from sources
Note that building an entire distribution is a long process. It also requires a big amount of free disk space.
The support for Microchip AT91 SoC family is included in a particular Yocto Project layer: meta-atmel. The source for this layer are hosted on Linux4SAM GitHub account![]() : https://github.com/linux4sam/meta-atmel
: https://github.com/linux4sam/meta-atmel![]()
Building environment
A step-by-step comprehensive installation is explained in the Yocto Project Quick Build![]() . The following lines have to be considered as an add-on that is AT91 specific or that can facilitate your setup.
. The following lines have to be considered as an add-on that is AT91 specific or that can facilitate your setup.
Prerequisite
Here are the reference pages for setting up a Yocto Project building environment: What You Need and How You Get It![]() .
.
![]() add
add git-lfs to the package requirement list from whichever Linux distribution you use.
For instance, on Ubuntu or debian, these packages need to be installed on your development host:
sudo apt-get install gawk wget git-core git-lfs diffstat unzip texinfo gcc-multilib \
build-essential chrpath socat cpio python3 python3-pip python3-pexpect \
xz-utils debianutils iputils-ping python3-git python3-jinja2 libegl1-mesa libsdl1.2-dev \
pylint3 xterm
Step by step build procedure
![]() here is a copy of the README
here is a copy of the README![]() procedure available directly in the
procedure available directly in the meta-atmel layer. This file in the meta-atmel layer repository must be considered as the reference and the following copy can be out-of-sync.
![]() starting with
starting with Linux4SAM 2021.04 release, the meta-atmel layer supports Yocto Project templates, so make sure you create a new build environment using oe-init-build-env
This layer provides support for Microchip microprocessors (aka AT91)
====================================================================
For more information about the Microchip MPU product line see:
http://www.microchip.com/design-centers/32-bit-mpus
Linux & Open Source on Microchip microprocessors:
http://www.linux4sam.org
Supported SoCs / MACHINE names
==============================
Note that most of the machine names below, have a SD Card variant that can be
built by adding an "-sd" suffix to the machine name.
- SAMA5D2 product family / sama5d2-xplained, sama5d2-xplained-emmc, sama5d27-som1-ek-sd, sama5d27-som1-ek-optee-sd, sama5d2-ptc-ek, sama5d2-icp, sama5d27-wlsom1-ek-sd, sama5d29-curiosity-sd
- SAMA5D4 product family / sama5d4ek, sama5d4-xplained
- SAMA5D3 product family / sama5d3xek, sama5d3-xplained
- AT91SAM9x5 product family (AT91SAM9G15, AT91SAM9G25, AT91SAM9X25, AT91SAM9G35 and AT91SAM9X35) / at91sam9x5ek
- AT91SAM9RL / at91sam9rlek
- AT91SAM9G45 / at91sam9m10g45ek
- SAM9X60 / sam9x60ek, sam9x60-curiosity
- SAMA7G5 / sama7g5ek-sd, sama7g5ek-optee-sd, sama7g5ek-emmc, sama7g5ek-ospi
- SAMA7D65 / sama7d65-curiosity
- SAM9X75 / sam9x75eb, sam9x75-curiosity
Sources
=======
- meta-atmel
URI: https://github.com/linux4sam/meta-atmel.git
Branch: scarthgap
Tag/commit:linux4microchip+sama7d65-2025.02
Dependencies
============
This Layer depends on :
- poky
URI: https://git.yoctoproject.org/poky
Branch: scarthgap
Tag:scarthgap-5.0.3
- meta-openembedded
URI: https://git.openembedded.org/meta-openembedded
Branch: scarthgap
Tag/commit:735ae0310870ffce07ce0c55c4f87c20ac161ff9
- meta-arm (for optee components)
URI: https://git.yoctoproject.org/meta-arm
Branch: scarthgap
Tag:yocto-5.0
Build procedure
===============
0/ Create a directory
mkdir my_dir
cd my_dir
1/ Clone yocto/poky git repository with the proper branch ready
git clone https://git.yoctoproject.org/poky && cd poky && \
git checkout -b scarthgap scarthgap-5.0.3 && cd -
2/ Clone meta-openembedded git repository with the proper branch ready
git clone git://git.openembedded.org/meta-openembedded && \
cd meta-openembedded && git checkout -b scarthgap 735ae0 && cd -
3/ Clone meta-atmel layer with the proper branch ready
git clone https://github.com/linux4sam/meta-atmel.git && cd meta-atmel && \
git checkout linux4microchip+sama7d65-2025.02 && cd -
4/ Clone meta-arm layer with the proper branch ready
git clone https://git.yoctoproject.org/meta-arm && cd meta-arm && \
git checkout -b scarthgap yocto-5.0 && cd -
5/ Enter the poky directory to configure the build system and start the build process
cd poky
If not created yet, add a new "build-microchip" directory:
mkdir build-microchip
Else, if it's the first time you use Yocto Project templates, and if the
build-microchip directory remains from a previous use, we advise you to start
from a fresh directory. Keep your build-microchip/conf/local.conf file for
reference.
6/ Inside the .templateconf file, you will need to modify the TEMPLATECONF
variable to match the path to the meta-atmel layer "conf" directory:
export TEMPLATECONF=${TEMPLATECONF:-../meta-atmel/conf/templates/default}
7/ Initialize build directory
source oe-init-build-env build-microchip
8/ To build a small image provided by Yocto Project:
[MACHINE=] bitbake core-image-minimal
Example for sama5d2-xplained-sd SD card image:
MACHINE=sama5d2-xplained-sd bitbake core-image-minimal
9/ To build the microchip image with no graphics support:
[MACHINE=] bitbake microchip-headless-image
Example for sama5d2-xplained-sd SD card image:
MACHINE=sama5d2-xplained-sd bitbake microchip-headless-image
10/ To build the microchip image with graphics support (EGT):
[MACHINE=] bitbake microchip-graphics-image
Example for sama5d2-xplained-sd SD card image:
MACHINE=sama5d2-xplained-sd bitbake microchip-graphics-image
Typical bitbake output
======================
Build Configuration:
BB_VERSION = "2.8.0"
BUILD_SYS = "x86_64-linux"
NATIVELSBSTRING = "universal"
TARGET_SYS = "arm-poky-linux-gnueabi"
MACHINE = "sam9x75-curiosity-sd"
DISTRO = "poky-atmel"
DISTRO_VERSION = "5.0.3"
TUNE_FEATURES = "arm armv5 thumb dsp"
TARGET_FPU = "soft"
meta
meta-poky
meta-yocto-bsp = "heads/scarthgap-5.0.3:0b37512fb4b231cc106768e2a7328431009b3b70"
meta-oe
meta-networking
meta-webserver
meta-python
meta-initramfs = "735ae0310870ffce07ce0c55c4f87c20ac161ff9:735ae0310870ffce07ce0c55c4f87c20ac161ff9"
meta-atmel = "heads/linux4microchip-2024.10:53c6bb2eddceb62ae5120c7c68174ce423d341e2"
meta-multimedia = "735ae0310870ffce07ce0c55c4f87c20ac161ff9:735ae0310870ffce07ce0c55c4f87c20ac161ff9"
meta-arm
meta-arm-toolchain = "heads/yocto-5.0:8aa8a1f17f5b64bc691544f989f04fc83df98adb"
Contributing
============
To contribute to this layer you should submit the patches for review to:
the github pull-request facility directly or the forum. Anyway, don't forget to
Cc the maintainers.
Microchip Forum:
https://www.microchip.com/forums/f542.aspx
for some useful guidelines to be followed when submitting patches:
http://www.openembedded.org/wiki/How_to_submit_a_patch_to_OpenEmbedded
Maintainers:
Hari Prasath G E
Nicolas Ferre
When creating patches insert the [meta-atmel] tag in the subject, for example
use something like:
git format-patch -s --subject-prefix='meta-atmel][PATCH'
Using SAM-BA to flash components to board
eMMC Flash demo
The layout of the eMMC Flash Demo is the same as on SD-Card.
Install SAM-BA software in your PC
In addition to the official SAM-BA pages on http://www.microchip.com![]() , we maintain information about SAM-BA in the SoftwareTools page.
, we maintain information about SAM-BA in the SoftwareTools page.
![]() use SAM-BA 3.8.y onwards. You can download it here: SAM-BA 3.8 release page
use SAM-BA 3.8.y onwards. You can download it here: SAM-BA 3.8 release page![]() .
.
Launch SAM-BA tools
- According to this section make sure that the chip can execute the SAM-BA Monitor.
In addition to the Qt5 QML language for scripting used for flashing the demos, most common SAM-BA action can be done using SAM-BA command line.
For browsing information on the SAM-BA command line usage, please see the Command Line Documentation that is available in the SAM-BA installation directory: doc/index.html or doc/cmdline.html .
SAM-BA includes command line interface that provides support for the most common actions:
- reading / writing to arbitrary memory addresses and/or peripherals
- uploading applets and using them to erase/read/write external memories
The command line interface is designed to be self-documenting.
The main commands can be listed using the "sam-ba --help" command:
SAM-BA Command Line Tool v3.8 Copyright 2024 Microchip Technology Usage: ./sam-ba [options] SAM-BA Command Line Tool Options: -v, --version Displays version information. -h, --help Displays this help. -t, --tracelevel <trace_level> Set trace level to <trace_level>. -L, --applet-buffer-limit <SIZE> Set applet buffer limit to <SIZE>
bytes (default 131072). -x, --execute <script.qml> Execute script <script.qml>. -p, --port <port[:options:...]> Communicate with device using <port>. -d, --device <device[:options:...]> Connected device is <device>. -b, --board <board[:options:...]> Connected board is <board>. -m, --monitor <command[:options:...]> Run monitor command <command>. -a, --applet <applet[:options:...]> Load and initialize applet <applet>. -c, --command <command[:args:...]> Run command <command>. -w, --working-directory <DIR> Set working directory to <DIR>.
Additional help can be obtained for most commands by supplying a "help" parameter that will display their usage.
For example "sam-ba --port help" will display:
Known ports: j-link, serial, secure
Command that take an argument with options (port, monitor, applet) will display even more documentation when called with "help" as option value.
For example "sam-ba --port serial:help" will display:
Syntax:
serial:[<port>]:[<baudrate>]
Examples:
serial serial port (will use first AT91 USB if found otherwise first serial port)
serial:COM80 serial port on COM80
serial:ttyUSB0:57600 serial port on /dev/ttyUSB0, baudrate 57600
Programming components into eMMC flash
Program rootfs file
With SAM-BA you can directly program SD/MMC images to the on-board eMMC. These images are named *.img or *.wic for the ones generated by Yocto Project.
# sam-ba -p serial -b sama7g5-ek -a sdmmc -c write:microchip-demo-image-sama7g5ek.wic Opening serial port 'ttyACM0' Connection opened. Detected memory size is 3925868544 bytes. Page size is 512 bytes. Buffer is 88576 bytes (173 pages) at address 0x0022a5a0. Executing command 'write:microchip-demo-image-sama7g5ek.wic' Wrote 88576 bytes at address 0x00000000 (0.02%) Wrote 88576 bytes at address 0x00015a00 (0.04%) Wrote 88576 bytes at address 0x0002b400 (0.05%) Wrote 88576 bytes at address 0x00040e00 (0.07%) Wrote 88576 bytes at address 0x00056800 (0.09%) [..] Wrote 88576 bytes at address 0x1d4e8600 (99.98%) Wrote 88576 bytes at address 0x1d4fe000 (100.00%) Wrote 4608 bytes at address 0x1d513a00 (100.00%) Connection closed.
![]() Note that programming a rootfs of several hundreds of MiB will take a few minutes to complete.
Note that programming a rootfs of several hundreds of MiB will take a few minutes to complete.
Recent FAQ
- Sama7g5-ek
-
• Wilc Faq: How to use WILC on SAM development boards. (Kernel)
• Media Controller: What is Media controller and how to use it with SAM products.. (linux-5.15-mchp, linux-6.1-mchp, linux-6.6-mchp)
• U-Boot FAQ: Some U-Boot FAQ entries. (U-Boot)
• Using FITwith Overlays: How to use U-boot with FIT image to load overlays. (U-Boot, Kernel)
• Patching DTin Uboot: How to apply DTBOs in U-boot. (U-Boot, Kernel)
• Using Systemd: Basic systemd user guide. (linux-6.1-mchp, linux-6.6-mchp, BuildRoot, YoctoProject)
• Thermal Faq: Thermal management support on SAMA7G5. (Kernel, linux-5.15-mchp, linux-6.1-mchp, linux-6.6-mchp)
• Using SAMA 5 D 2 ADCDevice: Using the SAMA5D2-compatible ADC device. (Kernel, linux-5.15-mchp, linux-6.1-mchp, linux-6.6-mchp)
• Using I 2 SC: How to use I2SC. (linux-5.10-at91, linux-5.15-mchp, linux-6.1-mchp, linux-6.6-mchp)
• ISCWhite Balance Features: White balance features of the Image sensor controller.. (Kernel, linux-4.19-at91, linux-5.4-at91, linux-5.10-at91, linux-5.15-mchp, linux-6.1-mchp, linux-6.6-mchp)
• Sama 7 g 5 Xisc: Detailed explanation of the sama7g5 image acquisition pipeline. (Kernel, linux-5.15-mchp, linux-6.1-mchp, linux-6.6-mchp)
• Sama 7 g 5 Ov 7740: Interfacing sama7g5 with parallel omnivision ov7740 sensor.. (Kernel, linux-5.15-mchp, linux-6.1-mchp, linux-6.6-mchp)
• Using ASRC: How to use ASRC. (Kernel, linux-5.15-mchp, linux-6.1-mchp, linux-6.6-mchp)
• Build Issue Buildroot G 1: Buildroot gst1-at91-gstreamer. (BuildRoot)
• Sama 7 g 5 Imx 274: using Sony IMX274 sensor with sama7g5. (linux-5.15-mchp, linux-6.1-mchp)
Linux4SAM
Boards
- SAMA7D65 Curiosity
- SAM9X75 Curiosity
- SAMA5D29 Curiosity
- SAM9X60 Curiosity
- SAMA7G5-EK
- SAMA5D2-ICP
- SAMA5D27 WLSOM1 EK
- SAM9X60-EK
- SAMA5D27 SOM1 EK
- SAMA5D2 PTC EK
- SAMA5D2 Xplained
- SAMA5D3 Xplained
- SAMA5D4 Xplained
- Older boards
FAQ
Useful links
- Microchip Microprocessors forums
- AT91 Community (archive)
- Microchip
- Linux4Microchip on GitHub
- Linux4SAM on GitHub
NAVIGATION
Copyright © by the contributing authors. All material on this collaboration platform is the property of the contributing authors.
Linux® is the registered trademark of Linus Torvalds in the U.S. and other countries.
Microchip® and others, are registered trademarks or trademarks of Microchip Technology Inc. and its subsidiaries. ![]()
Arm® and others are registered trademarks or trademarks of Arm Limited (or its affiliates). Other terms and product names may be trademarks of others.
Ideas, requests, contributions ? Connect to LinksToCommunities page.

